Description
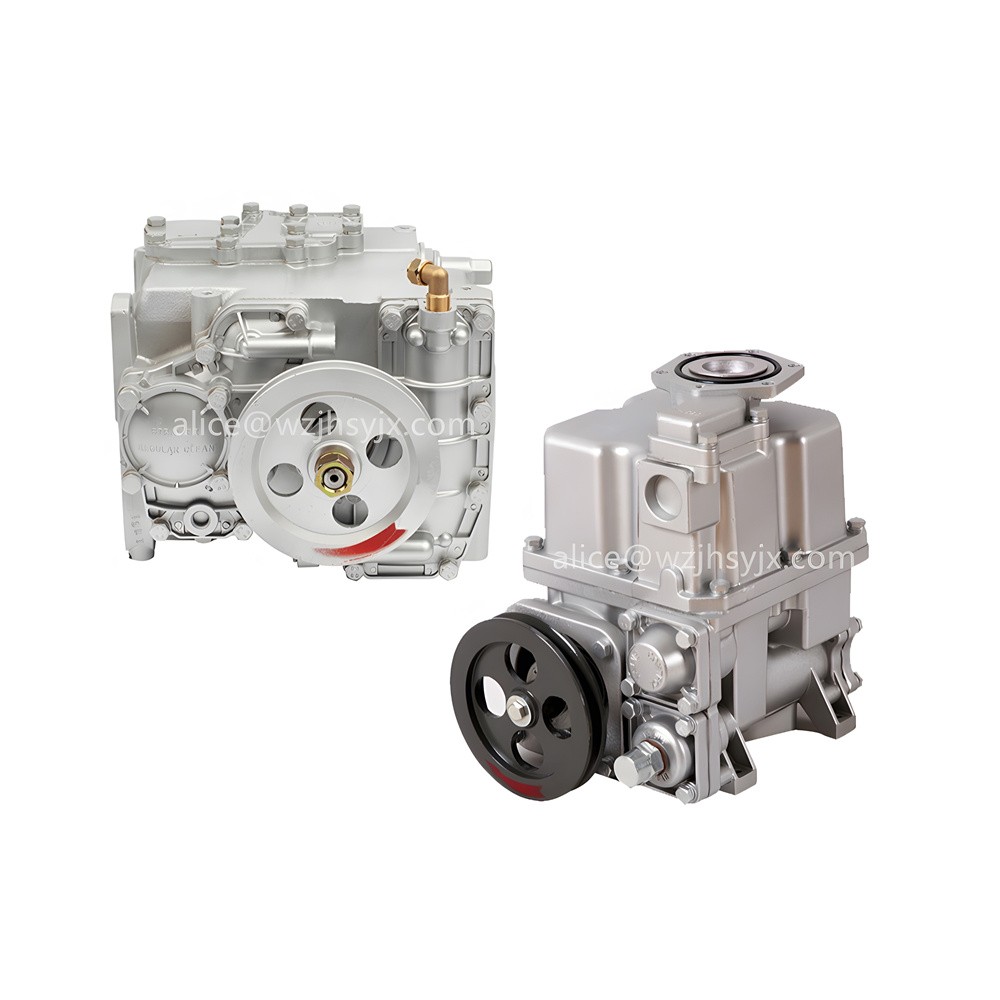
Combined Vane Pump Zyb-50 Oil Transfer Pump for Fuel Dispenser
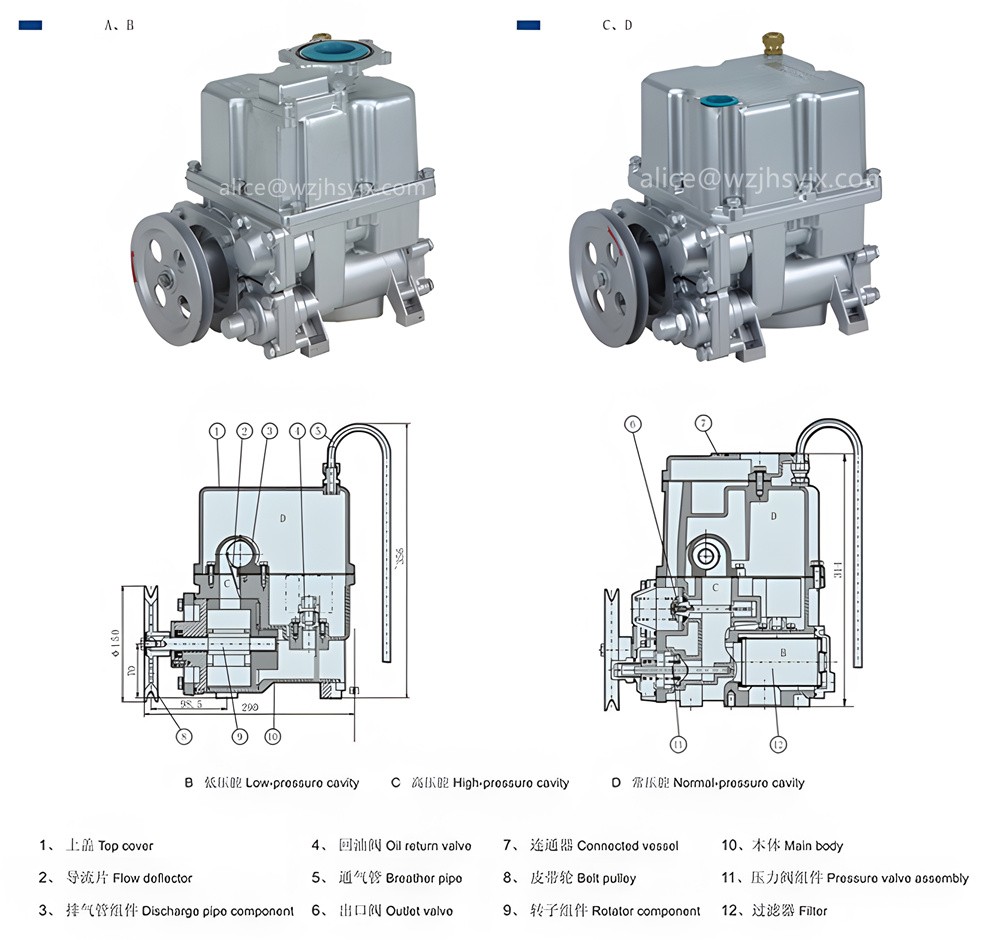
The combined vane pump ZYB-50/ZYB-80 has two upper cover structures, A and C, to choose from, suitable for connecting different pipelines. The pump has a built-in oil-gas separator and overflow valve, with the advantages of low noise, large flow and long life.
Working principle of vane pump
The combined vane pump is a component that combines the vane pump and the oil-gas separator into one. In terms of working principle, the combined vane pump can be divided into two main parts: the vane pump and the oil-gas separator. The vane pump assembly pressed into the combined pump housing is collectively referred to as the vane pump part together with the filter, overflow valve, oil outlet valve, etc. The part of the combined pump other than the vane pump part is the oil-gas separation part. The function of the oil-gas separator is to separate the gas in the oil and discharge it out of the machine, filter out impurities in the oil, and provide users with pure oil without gas and impurities.
The location of the filter is the low-pressure chamber, the oil inlet of the low-pressure chamber is connected to the bellows, and the connection of the oil-gas separation pipe is the high-pressure chamber. Generally, the lower part of one end of the oil-gas separation pipe is connected to the oil outlet of the vane pump, and the lower part of the other end is connected to the oil outlet of the vane pump. There is also an overflow valve behind the oil outlet valve that is connected to the oil outlet cavity. The cavity where the float is located is a normal pressure cavity, which is connected to the atmosphere through the exhaust pipe.
Working process of vane pump
When the high-pressure oil output by the vane pump enters the oil-gas separation pipe from the oil outlet of the pump, under the action of the guide plate at the entrance of the oil-gas separation pipe, most of the oil advances in a spiral along the inner wall of the oil-gas separation pipe, and finally flows from the oil outlet of the oil-gas separation pipe to the oil outlet valve. The gas mixed in the oil is concentrated in the middle of the official cavity because its density is lower than that of the oil, and finally discharged from the oil-gas separation pipe to the normal pressure cavity. After the oil-gas mixture enters the atmospheric cavity, the gas floats up and is discharged into the atmosphere through the exhaust pipe. The oil is stored in the normal pressure cavity.
When the oil accumulates to a certain amount, the float floats up, driving the connecting rod to open the oil return valve, and the oil flows to the low-pressure cavity through the oil return valve. When the oil level drops to a certain height, the float falls back under the action of gravity, the return oil valve closes the valve, and the return oil function stops.
When the rotor rotates continuously, the vane pump outputs oil with a certain pressure and flow rate. The size of the oil delivery pressure depends on the pressure adjustment state of the overflow valve and the load resistance. The pressure oil from the vane pump enters the oil-gas separation pipe for oil-gas separation. Part of the gas-free oil from the oil-gas separation pipe returns to the low-pressure chamber through the overflow valve, and the other part enters the Flow meter through the oil outlet valve.
When the oil nozzle is opened, the load resistance is very small, the pressure oil overcomes the spring force of the oil outlet valve, enters the Flow meter from the oil outlet valve, and the overflow valve is closed or slightly opened. When the oil nozzle is closed, the oil pressure increases, the overflow valve is fully opened, and the pressure oil in the high-pressure chamber flows to the inlet of the vane pump through the overflow valve and recirculates. Usually, adjusting the overflow valve stud can change the pressure and output flow of the hydraulic system.